The Intelligent Organ
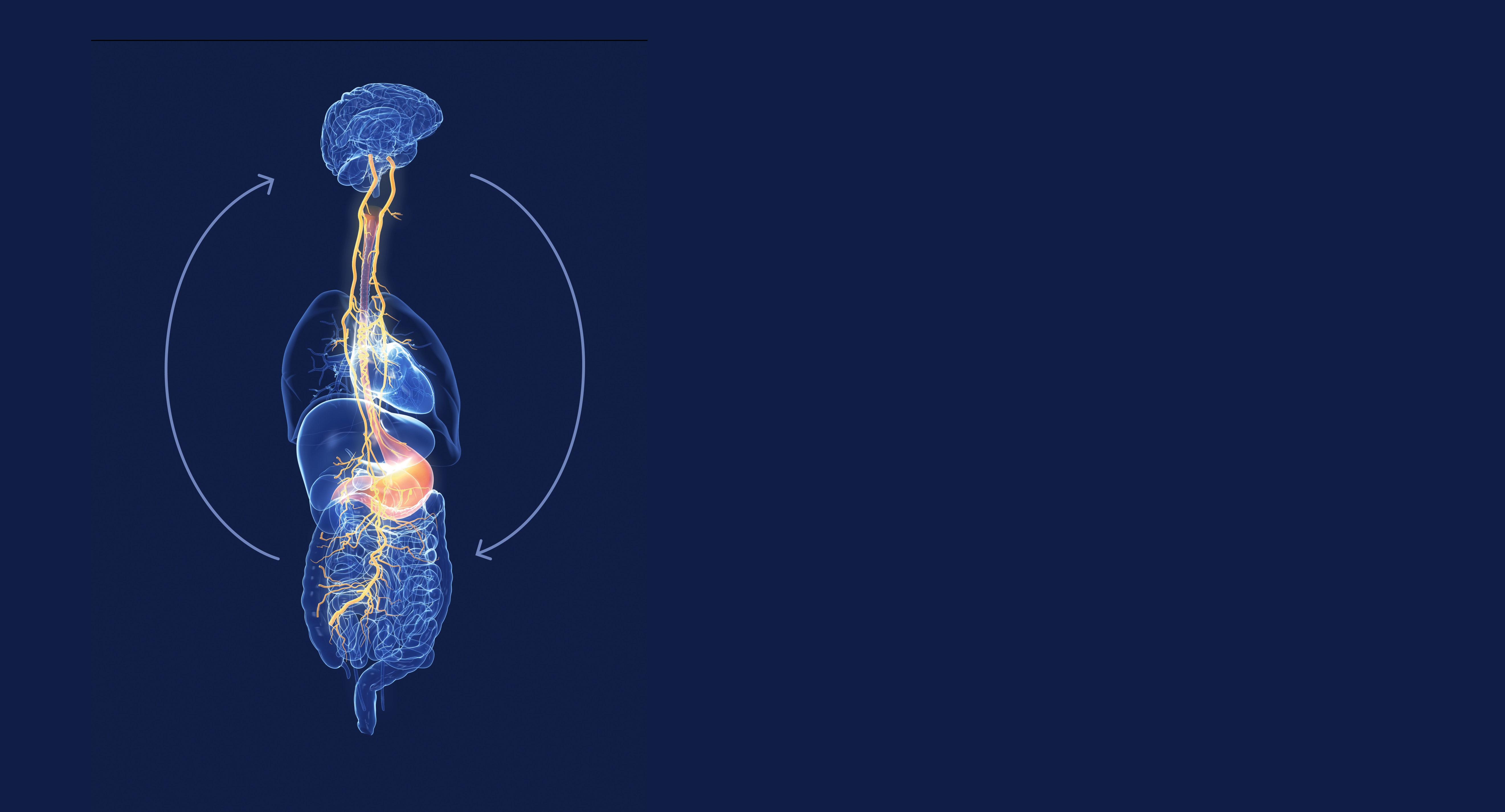
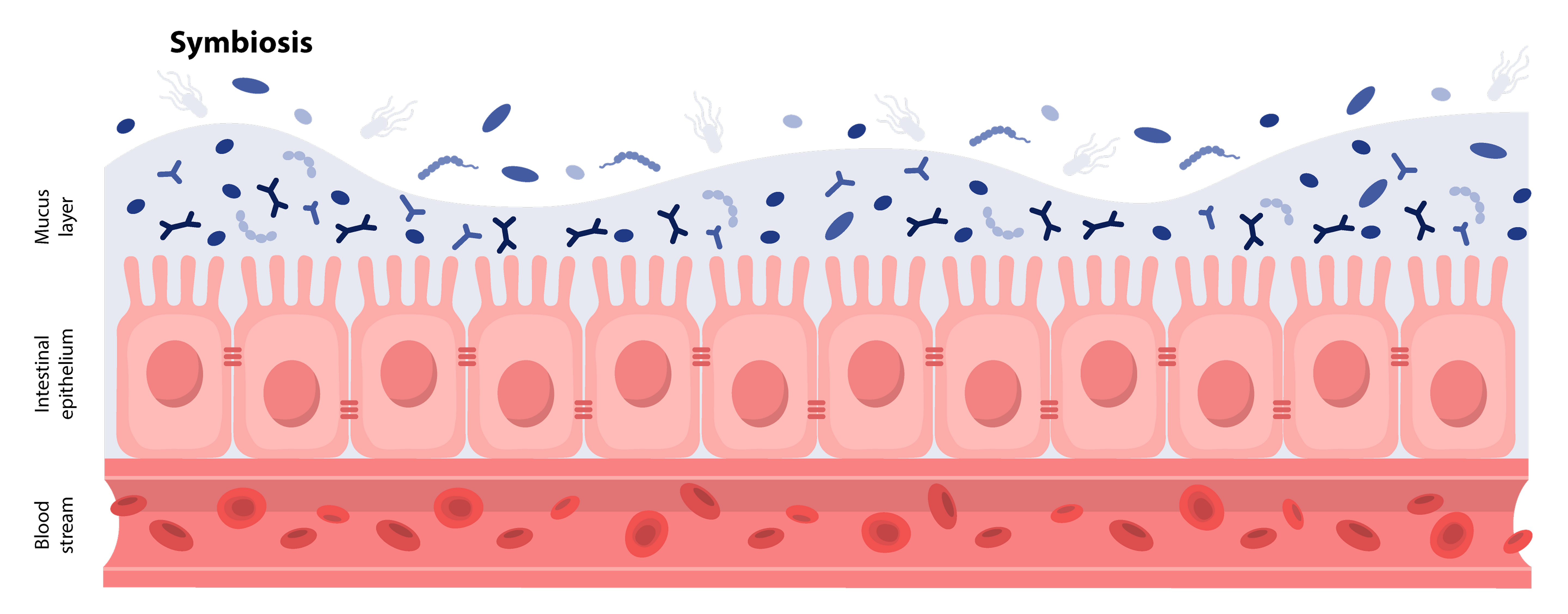
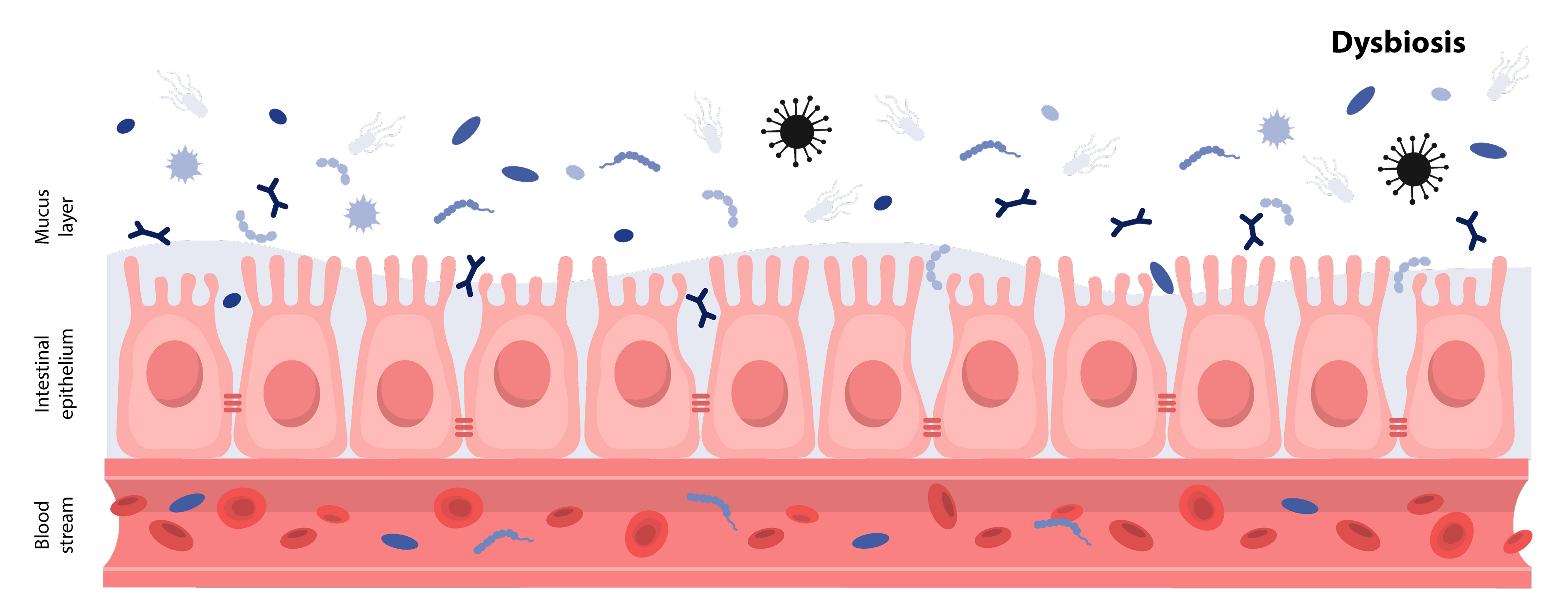
The gut is one of the body’s most complex and intelligent systems. It houses trillions of microorganisms that communicate with each other and with the body through a constant exchange of chemical signals. Together, they form the gut microbiome, a living ecosystem that influences nearly every biological process.
This network supports digestion, immunity, metabolism, and even emotional balance. Every meal, thought, and environmental change can reshape it within hours, showing how deeply the gut responds to daily life. Scientists now understand that the gut is not just a digestive tube but a biological command centre that regulates how we absorb nutrients, process energy, and defend against disease.
In this guide, we explore what the gut actually does, how it keeps you balanced, what happens when that balance is lost, and how modern science can measure it.